Chapter 4 - Lasers: Current Trends
(Sample page excerpted from book.)
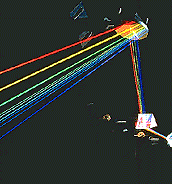
New CW Lasers Increase Productivity for Holographers
by Paul Ginouves
Until recently, successful use of holography in R&D or production applications usually required the use of an ion laser. The ion laser, in turn, required hands-on operator attention to maintain optimum alignment and achieve single-frequency operation. Fortunately, recent developments in laser technology have eliminated both these requirements. Specifically, ion lasers have undergone significant maturation in terms of ease of use and implementation, resulting in true “hands-free” operation, even for applications as demanding as holography. In addition, the diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) laser has now reached a performance level necessary for holographic use.
This article examines the “holographer-friendly” features that define the latest generation of ion lasers. It introduces DPSS laser technology, including its advantages and its current limitations. In addition, it will provide a look at a commercial holography application where the benefits of both laser types are critical enabling factors.
Ion Laser Maturity
The first argon ion laser was made in 1964. Ion lasers
opened the door to practical holography and have
dominated this application because of their low-noise,
high-power output
For shoppers with a limited budget, it also includes about acquiring surplus, used and repaired laser equipment.
characteristics. Indeed, photopolymers and other materials have been developed with sensitivities that specifically match ion laser wavelengths. As listed in Table 1, argon lasers can produce several watts of narrow-line output at several wavelengths in the UV through green. Krypton lasers have slightly lower output power, but can produce over 2 watts of single- frequency output in the red (647.1 nm) as well as lower powers at other visible wavelengths. Mixed gas (krypton/argon) lasers produce a combination of these output wavelengths.
(See top Coherent photo on the last page of the color picture section in this book.)
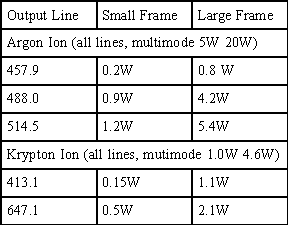
Table 1: Typical single frequency outputs for the higher power visible wavelengths of small frame and large frame ion lasers.
